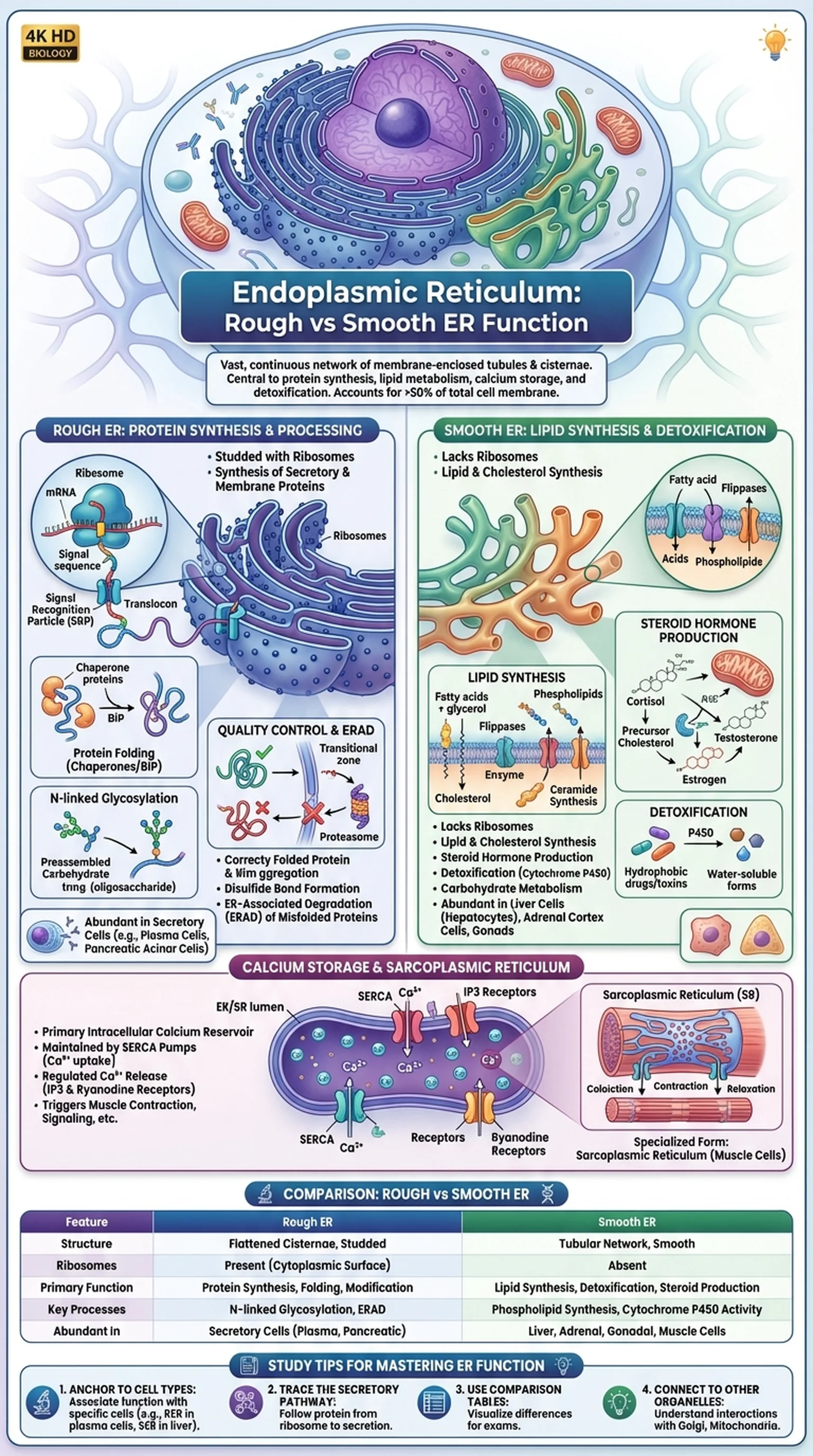
What Is the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a vast, interconnected network of membrane-enclosed tubules and flattened sacs called cisternae that extends throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. As one of the largest organelles by surface area, the endoplasmic reticulum plays central roles in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, calcium storage, and detoxification. Understanding ER function is fundamental to cell biology and appears frequently on exams such as the MCAT, AP Biology, and USMLE.
The endoplasmic reticulum is physically continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope, creating a direct structural connection between the nucleus and the cytoplasmic membrane system. This continuity allows newly transcribed mRNA to be translated by ribosomes on the ER surface almost immediately after export from the nucleus. The organelle function of the endoplasmic reticulum is so central to cellular operations that it typically accounts for more than half of the total membrane in a eukaryotic cell.
The endoplasmic reticulum exists in two morphologically and functionally distinct forms: rough ER and smooth ER. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface, giving it a granular appearance under the electron microscope. Smooth ER lacks ribosomes and has a more tubular morphology. Despite these differences, rough ER and smooth ER are continuous with each other and cooperate in numerous cellular processes. The relative proportion of each type varies depending on the cell's specialized function, reflecting the adaptability of this essential organelle.
Key Terms
A large network of membrane-enclosed tubules and cisternae in eukaryotic cells that functions in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, calcium storage, and detoxification.
Flattened, membrane-bound sacs that form the structural units of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
The specific biological role performed by a membrane-bound compartment within a cell, such as the protein-processing function of the endoplasmic reticulum.
The double membrane surrounding the nucleus that is continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum.