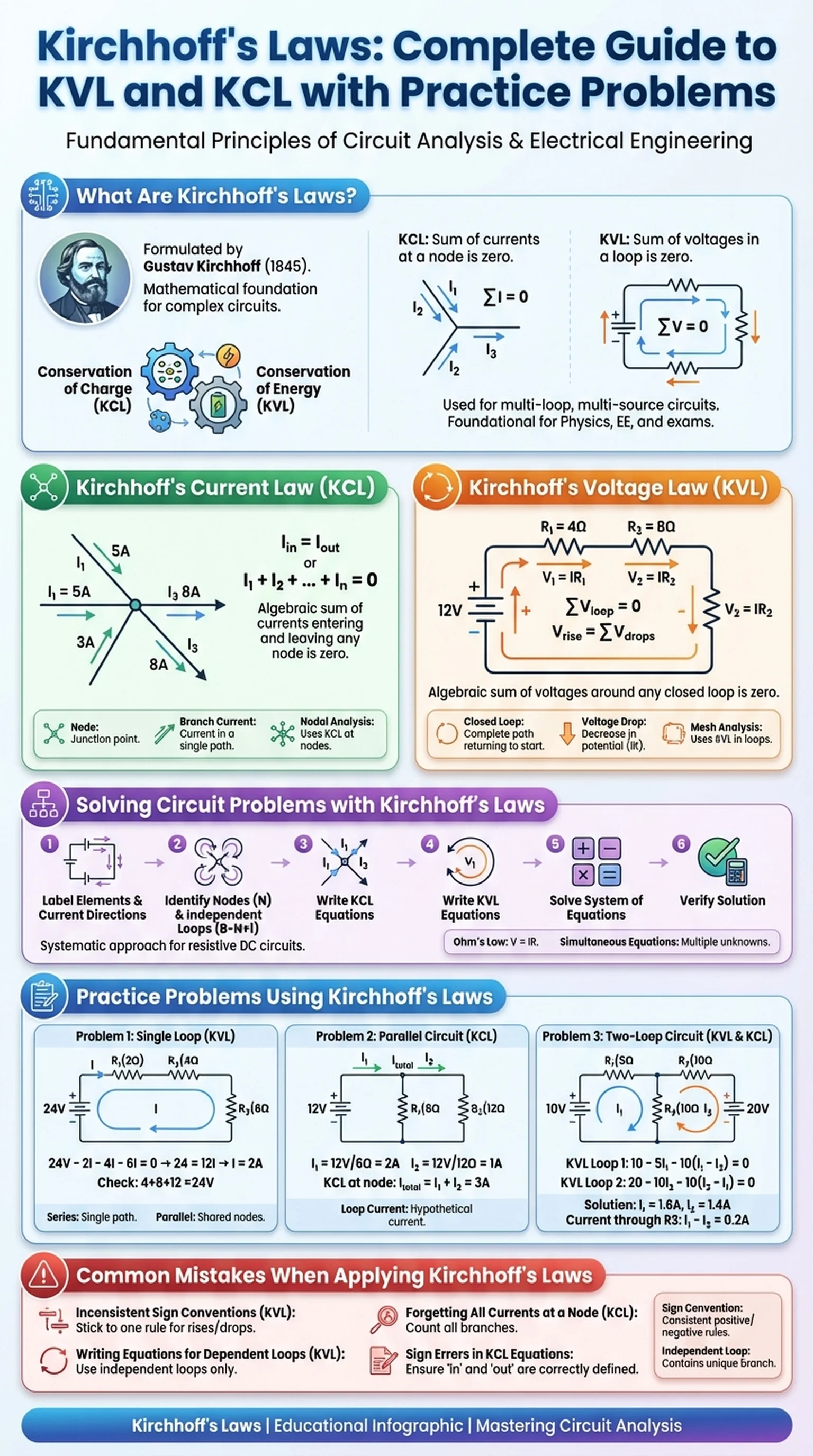
What Are Kirchhoff's Laws?
Kirchhoff's laws are two fundamental principles of electrical circuit analysis formulated by German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff in 1845. These laws — Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) — provide the mathematical foundation for analyzing any electrical circuit, no matter how complex. Together, they allow engineers and physics students to determine unknown currents, voltages, and resistances in circuits that cannot be simplified using series and parallel rules alone.
Kirchhoff's laws are built upon two conservation principles from physics. KCL is based on the conservation of electric charge, which states that charge cannot be created or destroyed. KVL is based on the conservation of energy, which states that the total energy gained by a charge traveling around a closed loop must equal the total energy lost. These conservation laws are among the most fundamental in all of physics, which is why Kirchhoff's laws have remained indispensable for over 175 years.
In practice, Kirchhoff's laws are essential for analyzing circuits that contain multiple loops, multiple sources, or combinations of components that do not reduce neatly into series or parallel configurations. While Ohm's law relates voltage, current, and resistance for a single component, Kirchhoff's laws provide the system of equations needed to solve for all unknowns in a multi-component circuit. They are foundational topics in introductory physics courses, electrical engineering programs, and standardized exams including the FE exam, the AP Physics exam, and the MCAT.
In the following sections, we will explore each of Kirchhoff's laws in detail, work through step-by-step examples of circuit analysis, and provide practice problems to help you master these essential tools. Whether you are a physics student encountering circuits for the first time or an engineering student preparing for professional licensure, a solid command of KCL and KVL will serve you throughout your career.
Key Terms
Two fundamental circuit analysis principles: Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL), based on conservation of charge and energy.
A German physicist who formulated the laws of circuit analysis in 1845, along with contributions to spectroscopy and thermal radiation.
The process of determining the voltages, currents, and power in each element of an electrical circuit.
The principle that electric charge cannot be created or destroyed, forming the basis of KCL.
The principle that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed, forming the basis of KVL.